平面双轴测试系统(Planar Biaxial Test System)
型号:Planar Biaxial Test System
联系人:李先生
联系电话:18618101725
品牌:biss
平面双轴测试系统(Planar Biaxial Test System)
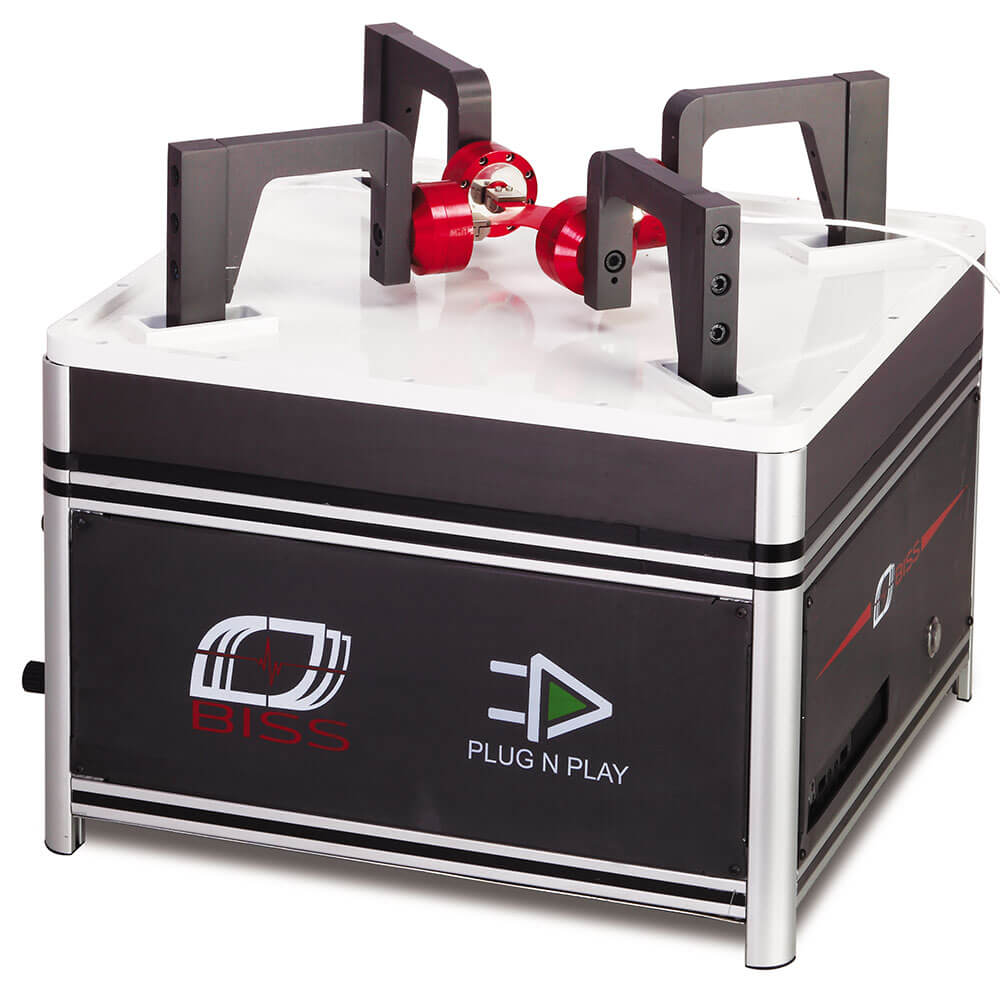
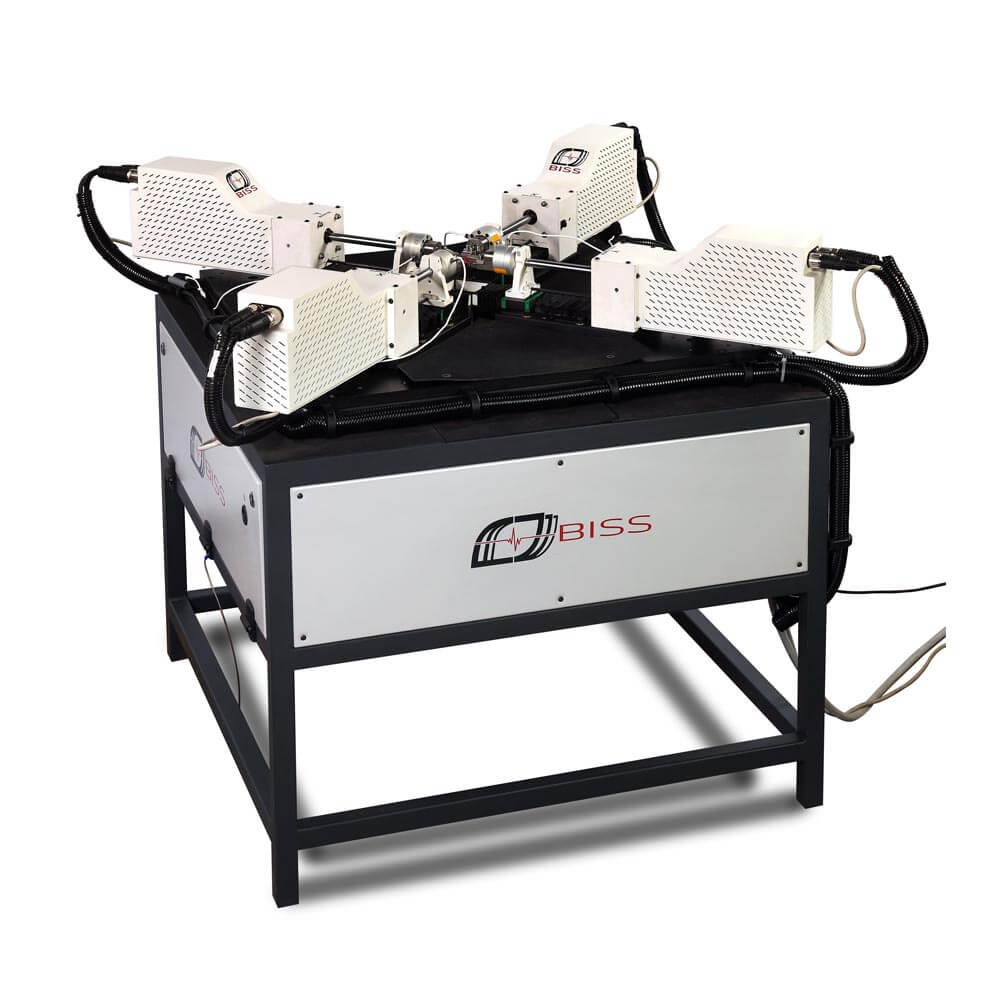
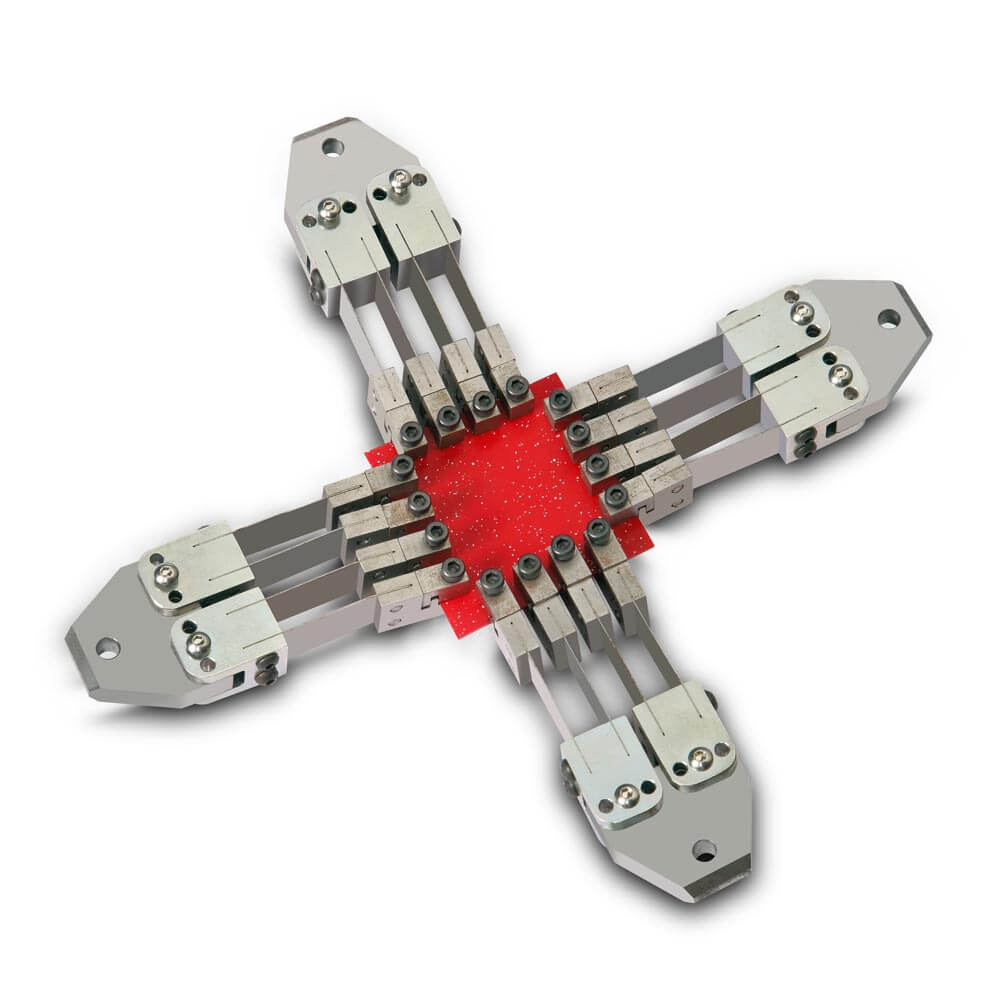


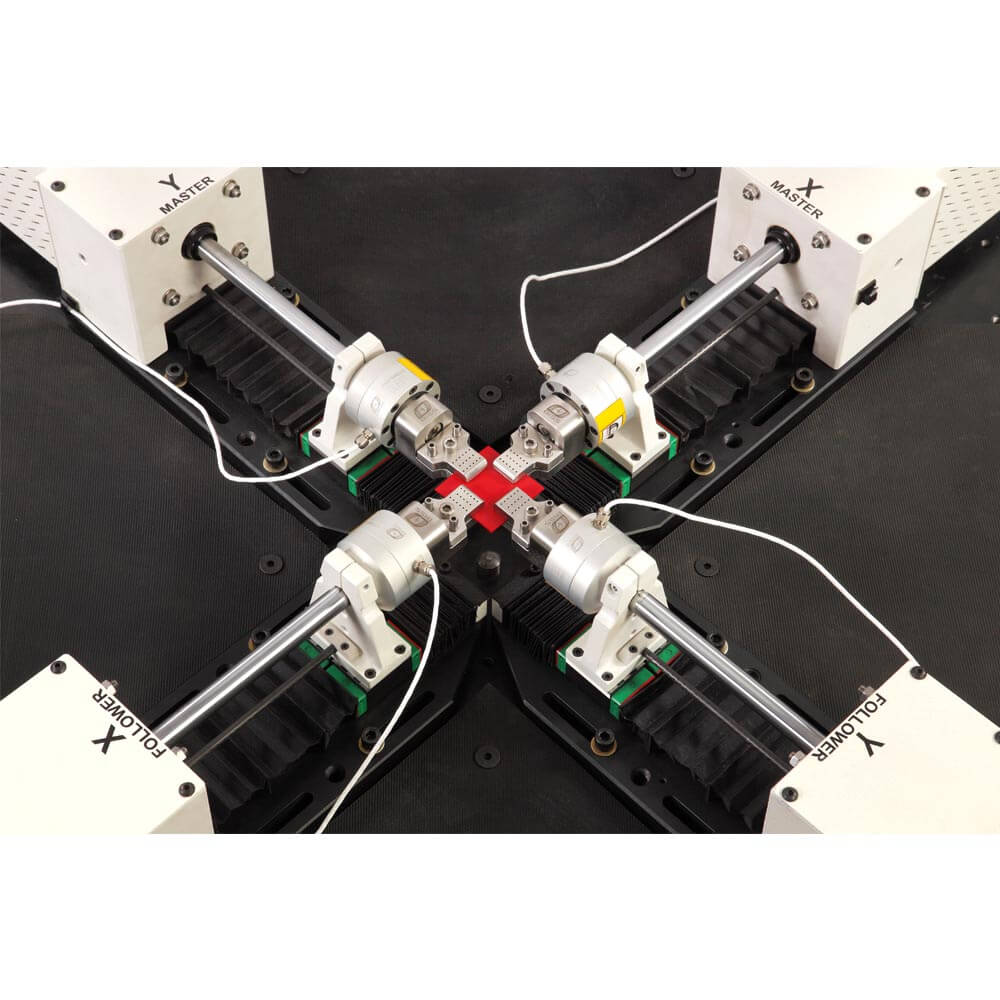

大多数实际情况涉及多轴载荷。例如,任何压力容器都会承受来自轴向和环向应力分量的双轴载荷。平面双轴测试系统由四个伺服执行器组成,这些执行器彼此成直角放置在立的自作用载荷框架上。平面双轴测试系统不同于轴向扭转系统。使用十字形样品。
平面双轴测试带来了许多挑战,因为负载的两个轴应能够以所需的模式(行程,负载或局部(轴向)应变响应)进行j确的立控制,并且在负载之间分配所需的负载和相位滞后轴。另一个挑战是将载荷限制在严格的双轴方向,而没有任何剪切分量,这不仅可能扭曲所需的应力状态,而且还可能对标距区域之外的样品造成意外损坏。
满足此要求的常规方法是在所谓的“主从”模式下驱动相对的执行器,从而使从器跟踪主执行器的位置,从而使被测样本中心的位置保持不变。
MA742密闭腔室套件,直径3毫米(用于MA626)
腔室由透明管制成(内径D = 3.2 mm),可在压缩过程中观察样品。 圆盘状样品被滑动活塞压缩,
液相可通过多孔盘(孔径为40微米)排出。
材质:不锈钢316L(多孔盘,孔径40微米)
直径:3.2毫米(内径)


MachOne分析软件-附加的wu限制和wu限制压缩(弹性)
该工具可以计算和可视化总模量(MPa),侧限压缩中样品的“应力松弛”曲线(毫米或力与时间的关系)计算出的
渗透率(mm2 / MPa·s)和拟合的均方误差(MSE)。
将曲线拟合到线性双相模型(Mow等,1980或Bursa等,1999),并引入圆盘的机械性能。
该模型非常适合用于容纳液体部分的样品的机械和描述的固体基质模型,为了获得有限压缩中的多孔弹性模型的结果。
MachOne ANALYSIS SOFTWARE - ADD-ON FOR UNCONFINED & CONFINED COMPRESSION (POROELASTIC)
MA726
This tool allows for the computing and visualizing of the aggregate modulus (MPa), the permeability (mm2/MPa·s) and the mean square error (MSE) of the fit calculated from a “Stress Relaxation” curve (load or force vs. time) in confined compression on a disk sample. The curve is fitted to the linear biphasic model (Mow et al., 1980 or Bursa? et al., 1999) in order to obtain the mechanical properties of the disk. Sample radius, strain and sample thickness need to be specified. This model is well adapted model for the mechanical description of samples containing a liquid fraction and a solid matrix, for example: cartilage or gel samples. A user license is required in order to obtain the results of the poroelastic model in confined compression (Software Add-On, contact BMM to obtain your license).
特征:
- 自反应双轴水平荷载框架
- 600 x 800 mm日光,用于抓握区域
- 线性轴承可保护称重传感器和执行器免受侧向载荷
- 伺服电动执行器组件,力为1 kN,额定行程为30mm
- 额定用于高达5 – 10 Hz的动态应用
- 内置光学编码器的大速度为0.1 m / s,分辨率为0.001 mm
- 1 kN动态容量的称重传感器
- 多通道控制系统和硬件
- 双轴视频引伸计(可选)
应用领域:
- 生物组织和生化构造的测试
- 软塑料,纤维,线束,电线的测试
- 屈服强度和j限强度
- 蠕变和粘弹性特征
- 疲劳特性
- 疲劳韧性和断裂力学
- 弹性模量
- 泊松比
- 热膨胀系数
- 反应特性
Planar Biaxial Test System
Most practical situations involve multi-axial loading. For example, any pressure vessel will see biaxial loading from the axial and hoop stress components. A planar biaxial test system consists of four servo-actuators positioned at right angles to each other on a free-standing self-reacting load frame. Planar biaxial test systems differ from axial-torsion systems. They involve the use of cruciform shaped specimens.
Planar biaxial testing poses a number of challenges in that the two axes of loading should be amenable to precise independent control in the desired mode (Stroke, Load or local (axial) strain response) and with desired distribution of load and phase lag between the two axes. Another challenge is to restrict loading to strictly biaxial, without any shear component whatsoever that may not only distort the desired stress state, but also threaten unintended damage to the specimen outside the gauge area.
The conventional approach to meeting this requirement is to drive opposing actuators in so called ‘Master-Slave’ mode, whereby the Slave tracks the position of the Master actuator, resulting in unchanged position of the perceived specimen center.
Features
- Self reacting biaxial horizontal load frame
- 600 x 800 mm daylight for gripping area
- Linear bearings to protect the load cell and actuators from side loads
- Servo electric actuator assembly with 1 kN force and 30mm stroke rating
- Rated for dynamic application up to 5 – 10 Hz
- Maximum speed of 0.1 m/s with built in optical encoder with a resolution of 0.001 mm
- Load cell of 1 kN dynamic capacity
- Multi channel control system & hardware
- Biaxial video extensometer (optional)
Applications
- Testing of biological tissues & biochemical constructs
- Testing of soft plastics, fibers, bundles, wires
- Yield and ultimate strength
- Creep and visco-elastic characteristics
- Fatigue characteristics
- Fatigue toughness and fracture mechanics
- Modulus of elasticity
- Poisson’s ratio
- Coefficient of thermal expansion
- Response characteristics