瑞士insphero GravityTRAP ULA 3D培养板-3D细胞悬滴培养板,insphero3D细胞悬滴培养板,3D INSIGHT PLATFORMS
型号:GravityTRAP
联系人:李胜亮
联系电话:18618101725
品牌: 瑞士insphero
3D细胞悬滴培养板——瑞士insphero品牌
GravityPLUS platform kit(货号:CS-06-001,规格10×96孔板)
GravityPLUS? and GravityTRAP? Trial Pack(货号:CS-00-020,规格1×96孔板)
Introductory GravityPLUS and GravityTRAP pack(货号:CS-06-010,规格3×96孔板)
瑞士insphero公司生产的3D细胞悬滴培养板wu需使用支架介质(scaffold-free),通过悬滴培养法(hanging-drop) ,就能将细胞悬液(一种细胞或多种细胞)形成3D微组织,3D微组织呈多细胞球状体,wu论在形态学上,还是在功能上均与自然组织类似。从而更好地模拟体内细胞生长情况,更直观的反映细胞生物学和功能,更准确的构建靶组织模型。
3D细胞培养板主要由GravityPlus板和GravityTRAP板组成,如下图:

GravityPlusTM板:采用细胞悬滴法(专利技术),使细胞形成球体状微组织(3D状态);将细胞悬液(一种细胞或多种细胞)添加到GravityPlusTM板中,2-4天,细胞在GravityPlusTM板中会形成微组织(微球状);
GravityTRAPTM板:采用非粘附包被技术,使微组织在wu依附、不解聚情况下培养数周,便于后续实验及检测。当微组织形成后,将其转移到GravityTRAPTM板中,可使微组织在wu依附、不解聚情况下培养数周,便于后续实验及检测。
应用实例
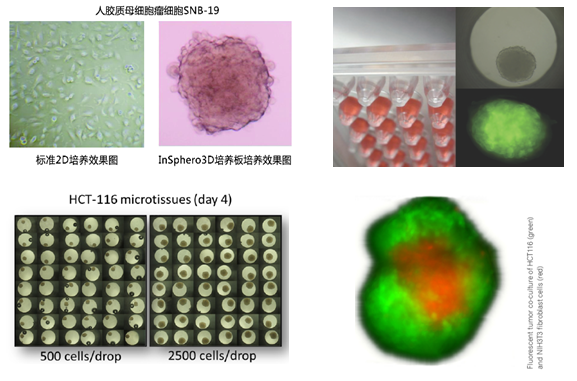
3D细胞悬滴培养板产品势及应用
1. 3D悬滴培养板形成的3D微组织呈多细胞球状体,wu论在形态学上,还是在功能上均与自然组织类似。
2. wu需支架介质,细胞可立体生长达数周,可对微组织多次用药
3. 可用于标准化学发光和荧光检测,可检测ATP、LDH、GSH和细胞凋亡等指标
4. 96孔板,j确的尺寸控制,孔间形成的微组织差异甚小,与高通量加样设备兼容,可用于高内涵分析(high content test)
5. 可用于几乎任何类型细胞的3D培养,如细胞系、原代细胞、干细胞及多种细胞共培养
6. 可用于癌症研究及药物分析,药物代谢动力学(DMPK),毒性测试(ADME-TOX)等
7. 如今,球大的前15家制药和护肤品企业均在使用InSphero的GravityPLUS?平台及3D微组织。产品质量符合ISO 9001:2008标准。
订购信息
3D悬滴培养板│GravityPLUS platform kit(货号:CS-06-001,规格10×96孔板)
3D悬滴培养板│GravityPLUS? and GravityTRAP? Trial Pack(货号:CS-00-020,规格1×96孔板)
3D悬滴培养板│Introductory GravityPLUS and GravityTRAP pack(货号:CS-06-010,规格3×96孔板)
Insphero公司简介
InSphero是通过类器官式3D微组织培养(supplier of organotypic, biological in vitro 3D microtissues)开展新药测试的领军型开发商。当前世界知名的前十家药物和护肤品制造商产品测试都使用到InSphero的专利微组织技术。
InSphero 3D Insight?微组织用于化学品应用的效能和毒理体外测试,包括长期效应和炎症介导的毒性效应。开发有可供选择的多种肿瘤和肝脏微组织产品及毒理测试模型(toxicology models in the pipeline)。InSphero 3D微组织较传统细胞模式更具有预测能力,培养持续时间更长,价格也更便宜。
InSphero由Jan Lichtenberg博士, Jens M. Kelm博士和Wolfgang Moritz博士等于2009年成立,是瑞士苏黎世联邦理工学院(Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich)和苏黎世大学(University Zurich)的衍生公司,总部设在Schlieren,在美国和德国设有分支机构。InSphero产品获多项国家和国际科学和商业化荣誉,产品质量符合ISO 9001:2008标准。
InSphero研发团队聚合在微组织工程,实验室自动化和微流体学的50多年丰富经验,带给客户新药测试上新的、更具洞悉力的体验。
应用文献:
Messner S, Fredriksson L, Lauschke VM, Roessger K, Escher C, Bober M, Kelm JM, Ingelman-Sundberg M, Moritz W. (2017) Transcriptomic, Proteomic, and Functional Long-term Characterization of Multicellular Three-Dimensional Human Liver Microtissues. Applied In Vitro Toxicology. doi: 10.1089/aivt.2017.0022.
Proctor WR, Foster AJ, Vogt J, Summers C, Middleton B, Pillings MA, Shienson D, Kijanska M, Stroebel S, Kelm JM, Morgan P, Messner S, Williams D. (2017) Utility of spherical human liver microtissues for prediction of clinical drug-induced liver injury. Arch Toxicol. Aug;91(8):2849-2863. doi: 10.1007/s00204-017-2002-1.
F. Paech, S. Messner, J. Spickermann, M. Wind, A.-H. Schmitt-Hoffmann, A.T. Witschi, B.A. Howell, R.J. Church, J. Woodhead, M. Engelhardt, S. Kr?henbühl, M. Maurer (2017) Mechanisms of hepatotoxicity associated with the monocyclic β-lactam antibiotic BAL30072. Arch. Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00204-017-1994-x..
Bruderer R., Bernhardt O.M., Gandhi T., Miladinovic S.M., Cheng L.Y., Messner S., Ehrenberger T., Zanotelli V., Butscheid Y., Escher C., Vitek O., Rinner O., and Reiter L. (2015). Extending the limits of quantitative proteome profiling with data-independent acquisition and application to acetaminophen treated 3D liver microtissues. Mol Cell Proteomics. May;14(5):1400-10. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.044305.
Bauer S, Wennberg Huldt C, Kanebratt KP, Durieux I, Gunne D, Andersson S, Ewart L, Haynes WG, Maschmeyer I, Winter A, ?mm?l? C, Marx U, Andersson TB (2017) Functional coupling of human pancreatic islets and liver spheroids on-a-chip: Towards a novel human ex vivo type 2 diabetes model. Sci Rep. Nov 6;7(1):14620. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14815-w.
Bader E, Migliorini A, Gegg M, Moruzzi N, Gerdes J, Roscioni SS, Bakhti M, Brandl E, Irmler M, Beckers J, Aichler M, Feuchtinger A, Leitzinger C, Zischka H, Wang-Sattler R, Jastroch M, Tsch?p M, Machicao F, Staiger H, H?ring HU, Chmelova H, Chouinard JA, Oskolkov N, Korsgren O, Speier S, Lickert H Identification of proliferative and mature ?-cells in the islets of Langerhans. Nature. 2016 Jul 21;535(7612):430-4. DOI: 10.1038/nature18624
Suter-Dick L., Alves P.M., Blaauboer B.J., Bremm K.D., Brito C., Coecke S., Flick B., Fowler P., Hescheler J., Ingelman-Sundberg M., Jennings P., Kelm J.M., Manou I., Mistry P., Moretto A., Roth A., Stedman D., van de Water B., and Beilmann M. (2015). Stem cell derived (SCD) systems in toxicology assessment. Stem Cells Dev. 2015 Jun 1;24(11):1284-96. doi: 10.1089/scd.2014.0540.
Herter S, Morra L, Schlenker R, Sulcova J, Fahrni L, Waldhauer I, Lehmann S, Reislander T, Agarkova I, Kelm JM, Klein C, Umana P, Bacac M. (2017). A novel three-dimensional heterotypic spheroid model for the assessment of the activity of cancer immunotherapy agents. Cancer Immunol Immunother. Jan; 66(1):129-140. doi: 10.1007/s00262-016-1927-1. Epub 2016 Nov 17.
Falkenberg, N., H?fig I, Rosemann M., Szumielewski J., Richter S., Schorpp K., Hadian K., Aubele M., Atkinson M.J., Anastasov N. (2016). Three-dimensional microtissues essentially contribute to preclinical validations of therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2016 Jan 14. doi: 10.1002/cam4.630. [Epub ahead of print]
Anastasov N., Hofig I., Radulovic V., Strobel S., Salomon M., Lichtenberg J., Rothenaigner I., Hadian K., Kelm J.M., Thirion C., Atkinson M.J. (2015). A 3D-microtissue-based phenotypic screening of radiation resistant tumor cells with synchronized chemotherapeutic treatment. BMC Cancer. Jun 10. 15:466. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1481-9.
Amann A., Zwierzina M., Gamerith G., Bitsche M., Huber J.M., Vogel G.F., Blumer M., Koeck S., Pechriggl E.J., Kelm J.M., Hilbe W. and Zwierzina H. (2014). Development of an innovative 3D cell culture system to study tumour–stroma interactions in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One.
Thoma C., Stroebel S., R?sch N., Calpe B., Krek W. and Kelm J.M. (2013). A High-Throughput–Compatible 3D Microtissue Co-culture System for Phenotypic RNAi Screening Applications. Journal of Biomolecular Screening.
Muoth C, Wichser A, Monopoli M, Correia M, Ehrlich N, Loeschner K, Gallud A, Kucki M, Diener L, Manser P, Jochum W, Wick P, Buerki-Thurnherr T (2016). A 3D co-culture microtissue model of the human placenta for nanotoxicity assessment. Nanoscale. 2016 Oct 6;8(39):17322-17332. doi: 10.1039/c6nr06749b
Falkenberg, N., H?fig I, Rosemann M., Szumielewski J., Richter S., Schorpp K., Hadian K., Aubele M., Atkinson M.J., Anastasov N. (2016). Three-dimensional microtissues essentially contribute to preclinical validations of therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2016 Jan 14. doi: 10.1002/cam4.630.
Anastasov N., Hofig I., Radulovic V., Strobel S., Salomon M., Lichtenberg J., Rothenaigner I., Hadian K., Kelm J.M., Thirion C., Atkinson M.J. (2015). A 3D-microtissue-based phenotypic screening of radiation resistant tumor cells with synchronized chemotherapeutic treatment. BMC Cancer. Jun 10. 15:466. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1481-9.
Amann A., Zwierzina M., Gamerith G., Bitsche M., Huber J.M., Vogel G.F., Blumer M., Koeck S., Pechriggl E.J., Kelm J.M., Hilbe W. and Zwierzina H. (2014). Development of an innovative 3D cell culture system to study tumour–stroma interactions in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 2014 Mar 24;9(3):e92511. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092511
Kim J., Fluri D.A., Marchan R., Boonen K., Mohanty S., Singh P., Hammad S., Landuyt B., Hengstler J.G., Kelm J.M., Hierlemann A., and Frey O. (2015). 3D spherical microtissues and microfluidic technology for multi-tissue experiments and analysis. J Biotechnol. Jan 12. pii: S0168-1656(15)00012-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.01.003.



